How Using A Private Network Address On iPhone Works (And Why You Should)
Apple tends to keep most of its convenient features, like AirDrop, locked to its own hardware, but this is also what allows its products to offer some of the best security features in the space. iPhones have always been praised for the several privacy-oriented settings they come with, and it’s good to see that Apple isn’t slowing down in this regard. Take, for instance, the Advanced Tracking and Fingerprinting Protection feature in iOS 26, which is a new addition.
Another privacy measure that modern iPhones use is private network addresses. To understand how this feature works, let’s get the fundamentals out of the way. Every smart device has a MAC (Media Access Control) address, which it uses to identify itself to every Wi-Fi network it connects to. In simpler words, a MAC address acts like a digital fingerprint for your device. Routers require a device’s MAC address to assign it an IP address and allow device filtering. Typically, MAC addresses don’t change, but there are ways you could spoof them for added privacy gains.
This is exactly what the Private Wi-Fi Address feature on iOS does. Instead of using the same hardware MAC address across all networks, the feature generates a unique MAC address for your device for each Wi-Fi network it connects to. This prevents possible triangulation that bad actors can exploit to track your device’s network activity. The feature is turned on by default, and Apple recommends you leave it on for better privacy.
Can you turn off Private Wi-Fi Address on iOS?
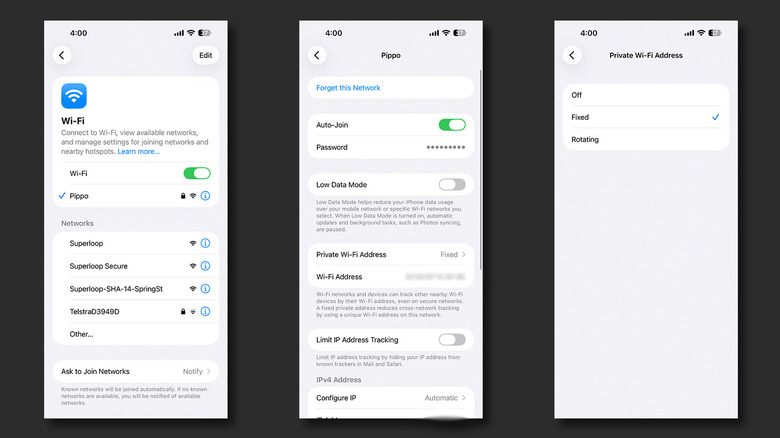
The Private Wi-Fi Address feature is available not just on iPhone, but also on iPad, Mac, and Apple Watch. It’s a toggle that can be configured on a per-network basis, and is set to the “Fixed” option by default. You can also switch to a “Rotating” private address that works by alternating between different MAC addresses every two weeks. Leaving this feature turned on is what’s recommended, but you might run into situations where it acts as an obstruction.
If you are unable to join a network or access the internet despite being connected to Wi-Fi, Apple first recommends you update your iPhone to the latest version of iOS. You can check for updates by navigating to Settings > General > Software Update. If this yields no positive results, you might find better luck turning off the Private Wi-Fi Address feature. To do so, follow these steps:
- Navigate to Settings > Wi-Fi.
- Locate the Wi-Fi network you wish to disable this feature for. You do not need to be connected to it.
- Tap on the “i” icon next to the Wi-Fi network’s name.
- Tap on “Private Wi-Fi Address” and change this setting to “Off.”
- Try reconnecting to this Wi-Fi network. Alternatively, you can tap on “Forget this Network” and connect to it again.
Since private addresses can be configured for every Wi-Fi network, leaving them turned off for a trusted home or work network isn’t going to pose major risks.
Other network settings on iOS for better privacy
Beyond allowing you to mask your device’s MAC address, iOS offers other network-related toggles that can help you strengthen your iPhone’s connection with Wi-Fi networks. Right below the Private Wi-Fi Address option, you will find a “Limit IP Address Tracking” toggle. Unlike MAC addresses, an IP address can be directly used to find a user’s approximate location. This toggle will hide your device’s IP address from known trackers when using Safari or the Mail app.
Another common acronym you’ll come across when tinkering with network settings is DNS. It stands for “Domain Name System” and essentially translates domain names to their respective numeric IP addresses. Switching to a different DNS service can offer better privacy and browsing speeds. Cloudflare’s 1.1.1.1 DNS address is a popular alternative and can be set up via the dedicated app available on the App Store. Alternatively, you can navigate to your Wi-Fi network’s settings, tap on “Configure DNS,” select “Manual,” and add a new server from here.
If you are subscribed to one of the iCloud+ plans, you get access to another privacy-oriented feature called Private Relay. This feature encrypts the traffic leaving your iPhone, which cloaks your IP address from websites. You can toggle this on by navigating to Settings > iCloud > Private Relay.


Comments are closed.